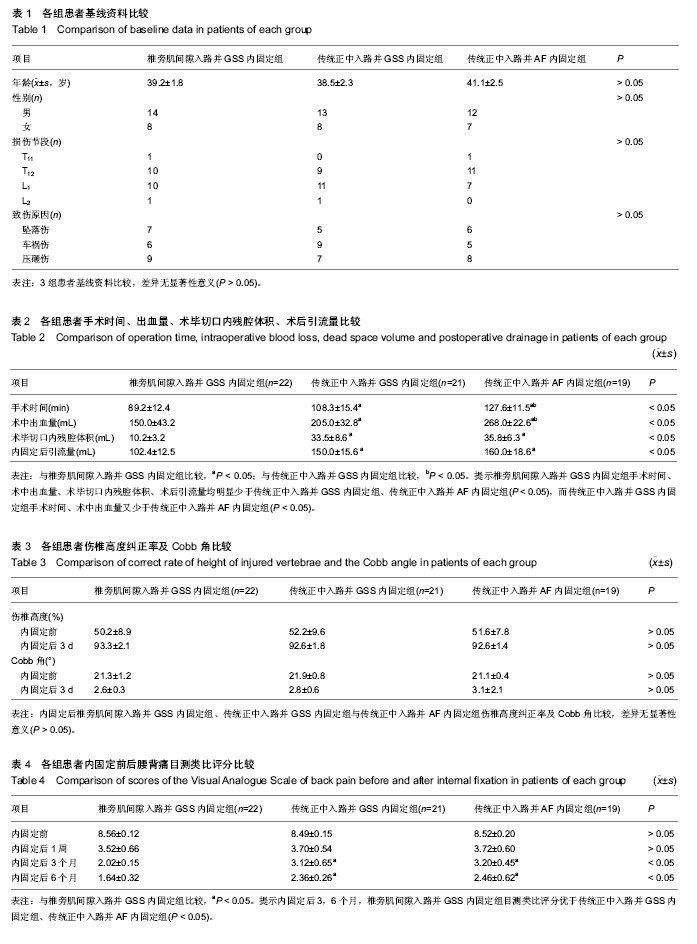
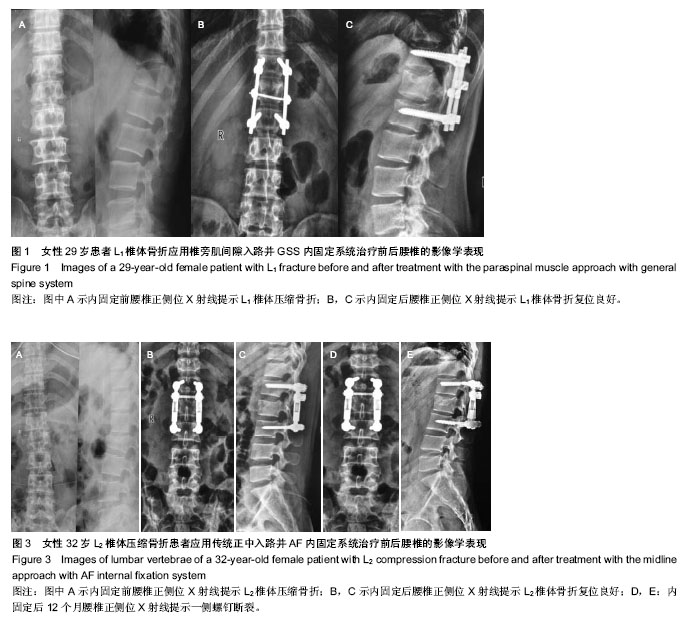
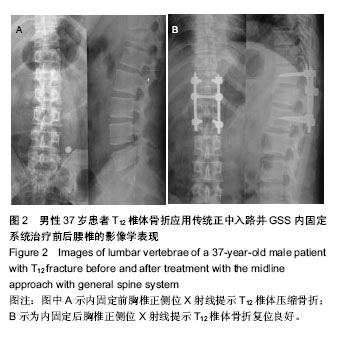
| [1] 王旭,李永民,谷守山.椎弓根钉置入内固定治疗胸腰椎骨折的应用进展[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(22): 4109-4112.
[2] Gejo R, Kawaguchi Y, Kondoh T, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging and histologic evidence of postoperative back muscle injury in rats. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2000;26(8): 941-946.
[3] Gejo R, Matsui H, Kawaguchi Y, et al. Serial changes in trunk muscle performance after posterior lumbar surgery.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1999;24(10):1023-1028.
[4] Kawaguchi Y,Matsui H, Gejo R,et al. Preventive measure of back muscle injury after posterior lumbar spine surgery in rates.Spine. 1998;23(21):2282-2287.
[5] Stevens KJ, Spenciner DB, Griffiths KL,et al. Comparison of minimally invasive and conventional open posterolateral lumbar fusion using magnetic resonance imaging and retraction pressure studies.Spinal Disord Tech. 2006;19(2):77-86.
[6] Wiltse LL, Bateman JG, Hutchinson RH, et al.The paraspinal sacrospinalis-splitting approach to the lumbar spine. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1968;50(5): 919-926.
[7] 肖宇龙,霍洪军,杨学军.AF系统治疗胸腰椎骨折的远期疗效分析[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2005,20(2):122-123.
[8] 吴雎,易晓文,吴光辉,等.应用AF系统治疗胸腰椎不稳定骨折17例临床分析[J].局解手术学杂志,2005,14(6):374-375.
[9] 王相利,汤继文,夏萍.胸腰段脊柱爆裂骨折伴脊髓损伤的治疗[J].中国综合临床,2004,20(5):453.
[10] 杨新武,赵春林,刘连升.椎弓根钉治疗不稳定胸腰椎骨折临床研究[J].中国基层医药,2007,14(5):830-831.
[11] 肖旭阳,王晓东,藏东玉.椎弓根螺钉在胸腰椎骨折置入内固定治疗中的应用及其生物相容性[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2010,14(26):4878-4881.
[12] 陈世忠.早期手术治疗胸腰椎爆裂性骨折的临床研究[J].中国医药导报,2010,7(13):19-21.
[13] 林慰光,林本丹,胡奕山.不同改良后路术式在胸腰椎骨折中的应用[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2009,17(24):1879-1882.
[14] 黄俊文,梁惠钦,胡曙荣.后入路手术治疗胸腰段爆裂性骨折[J].临床骨科杂志.2006, 9(4):337-338.
[15] Huskisson EC.Measurement of pain. Lancet. 1974;2(7889): 1127-1131.
[16] Watkins MB. Posterolateral bonegrafting for fusion of the lumbar and lumbosacral spine. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1959; 41(3): 388-396.
[17] Guyer DW, Wiltse LL, Peek RD. The Wiltse pedicle screw fixation system. Orthopedics.1988;11(10): 1455-1460.
[18] 方向前,胡志军,范顺武,等.胸腰段骨折经肌间隙入路与传统入路内固定的比较研究[J].中华骨科杂志,2009,29(4):315-319.
[19] Schwender JD, Holly LT,Rouben DP,et al. Minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion(TLIF):technical feasibility and initial results. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2005; 18(Suppl 1):S1-S6.
[20] Boelderl A,Daniaux H,Kathrein A,et al. Danger of damaging the medial branches of the posterior rami of spinal nerves during a dorsomedian approach to the spine.Clin Anat. 2002; 15(2):636-644.
[21] Onesti ST. Failed back syndrome. Neurologist. 2004;10(5): 259-264.
[22] Sihvonen T, Herno A, Paljarvi L, et al. Local denervation atrophy of paraspinal muscles in postoperative failed back syndrome. Spine. 1993;18(5): 575-581.
[23] Suwa H, Hanakita J, Ohshita N, et al. Postoperative changes in paraspinal muscle thickness after various lumbar back surgery procedures. Neurol Med. 2000;40(3): 151-154.
[24] Kawaguchi Y, Matsui H, Tsuji H. Back muscle injury after posterior lumbar spine surgery. Part 1:Histologic and histochemical analyses in rats. Spine. 1994;19(22): 2590-2597.
[25] 张玉坤,盛伟斌,唐庆,等,骨科手术风险度评分的建立及效能评价[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2012.20(18):1647-1652.
[26] Moseley GL,Hodges PW,Gandevia SC. Deep and superficial fibers of the lumbar multifidus muscle are differentially active during voluntary armmovements. Spine. 2002;27(2):E29-36.
[27] 李宏斌,张建华,李玉前,等.椎旁肌间隙入路在胸腰椎骨折手术中的应用[J].江苏医药,2009,35(10):1218-1219.
[28] 邓红平,胡灏,林格生,等.胸腰椎骨折后路内固定两种显露方式疗效比较[J].临床骨科杂志,2011,14(1):15-17.
[29] 麦荫文,韦文,黄承夸,等.经后路椎弓根钉棒系统内固定治疗胸腰椎骨折的疗效观察[J].广西医学,2011,33(8):1026-1027.
[30] 李书纲,邱贵兴,翁习生,等.通用型脊柱内固定系统椎弓根螺钉的生物学测试[J].中华骨科杂志,2002,22(4):229-232.
[31] 李书纲,邱贵兴,翁习生,等.通用型脊柱内固定系统椎弓根螺钉翻修作用的生物力学研究[J].中华骨科杂志,2002,22(11): 648-652.
[32] 谈国明,金荣忠,吴一雄,等. GSS-Ⅱ通用脊柱内固定系统在胸腰椎骨折治疗的应用[J].骨与关节损伤杂志,2004,19(4):262.
[33] 李书纲,邱贵兴,田野,等.通用型脊柱内固定系统稳定性的生物力学评价[J].中华外科杂志,2003,41(8):581-585.
[34] 李福民,任恒宽,黄尧.AF系统内固定治疗胸腰椎骨折48例体会[J].甘肃医药,2009,28(2):132-133.
[35] 曹晓东,杨秀莲.腰椎骨折AF钉内固定术治疗的临床分析[J].中国当代医药,2010,17(4):24-25. |